ICD Implantation Surgery in Nagpur

An Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillator (ICD) is a life-saving device that plays a crucial role in monitoring and regulating heart rhythms. It is particularly vital for individuals at risk of dangerous irregular heartbeats, such as ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. It consists of a pulse generator and leads implanted in the heart. The procedure involves making a small incision, inserting the leads, and connecting them to the generator.
This device continuously monitors the heart’s rhythm and delivers electric shocks when irregular heartbeats are detected. There are two primary types of Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator surgery:
- Traditional ICD: This type is placed in the chest, with wires (leads) connecting to the heart.
- Subcutaneous ICD (S-ICD): Positioned under the skin beside the chest below the armpit, the S-ICD does not touch the heart directly.
Procedure of ICD implantation
The ICD implantation procedure involves surgically placing an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) into a patient’s body. This device monitors and treats serious heart rhythm disorders. During the procedure:
- The patient is prepared and given anesthesia.
- A small incision is made, usually near the collarbone.
- Thin wires called leads are inserted and guided into the heart.
- The pulse generator, containing the device’s components, is implanted under the skin.
- Testing ensures proper device function.
- The incision is closed, and the patient recovers with follow-up appointments to monitor the ICD’s performance and overall heart health.
While generally safe and effective, there are potential risks and complications to consider. Patients should discuss these with the healthcare provider before the procedure.
Benefits of ICD implantation
The primary benefits of ICD implantation include:
– Immediate response to irregular heart rhythms.
– Prevention of sudden cardiac death.
– Increased survival rates for those at high risk of ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation.
– Customizable programming to match individual heart rhythm needs.
Why ICD implantation done?
Implantable cardioverter defibrillator uses include monitoring and regulating heart rhythm in individuals at high risk of sudden cardiac death due to specific heart conditions and are programmable to suit each patient’s needs.
These situations may include:
– Surviving cardiac arrest.
– Having a history of coronary artery disease and a weakened heart.
– Enlarged heart muscles.
– Genetic heart conditions that increase the risk of fast heart rhythms.
The ICD constantly monitors heart activity and provides immediate intervention, significantly reducing the risk of sudden death from cardiac arrest compared to medication alone.
What are the Risks Involved in ICD implantation?
While ICD implantation is a life-saving procedure, it carries certain risks, including:
– Infection at the implant site.
– Swelling, bleeding, or bruising.
– Blood vessel damage from ICD wires.
– Bleeding around the heart (potentially life-threatening).
– Movement of the device or leads, causing heart muscle damage (rare).
– Collapsed lung.
What is ICD Implantation Expense in India?
The Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator cost in India can vary widely based on factors such as brand, model, and features. The cost ranges from approximately 3.5 to 7.5 lakhs of rupees, including Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator price, implantation procedure, hospital fees, and medical professional charges. Health insurance coverage and individual circumstances can affect out-of-pocket expenses.
Types of ICD Implantation Surgery
There are several types of ICD implantation surgeries based on the procedure and device used:
Transvenous ICD Placement
This is the most common type of ICD implantation. It involves making an incision near the collarbone, inserting leads (wires) through veins into the heart, and connecting them to the ICD device, which is placed under the skin.
Subcutaneous ICD Placement
S-ICD placement involves positioning the device under the skin without placing leads inside the heart. The leads are instead placed along the chest wall, providing defibrillation without entering the heart.
Biventricular ICD Placement
or patients with heart failure and specific types of arrhythmias, a CRT-D device might be recommended. This involves placing leads in both ventricles of the heart to synchronize heartbeats and improve pumping efficiency, in addition to providing defibrillation.
What Happens After the ICD implantation?
Following ICD implantation, patients can expect the following:
– The area around the ICD site may be swollen and tender for a few days or weeks.
– Pain management may be necessary.
– Limitations on arm movements for about eight weeks to prevent wire movement.
– Avoidance of certain activities, such as heavy lifting and energetic sports.
– Regular check-ups to monitor ICD function and battery status.
Implantable cardioverter defibrillators are remarkable devices that offer a lifeline to individuals at risk of life-threatening heart arrhythmias. While they come with potential risks, the benefits in terms of life-saving capabilities far outweigh these concerns. Close collaboration between patients and healthcare providers ensures the best possible outcome when considering and living with an ICD.
Our Medical Services

ECG
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is one of the only and speediest tests utilized to survey the heart. Anodes (small, plastic patches that stick to the skin) are set at certain spots on the chest, arms, and legs.
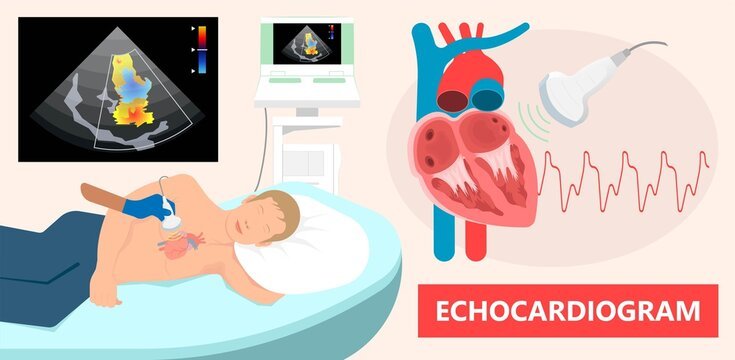
2D Echo
A two-dimensional Echocardiogram or 2D Echo test is a demonstrative test that employs ultrasound waves to evaluate the working of the heart.

Holter Monitoring
Holter monitoring measures your heart activity over an extended period, usually between 24 and 48 hours. Basically, a Holter Monitoring is a portable device which records the heart’s electrical signals.

BP Monitoring
Each time your heart beats, it pumps blood into your arteries. A blood pressure measurement may be a test that measures the force (pressure) in your arteries as your heart pumps.

Coronary Angiography
Coronary angiography diagnoses and evaluates coronary artery blockages. Contrast dye is injected into arteries, enabling X-ray imaging to visualize blood flow and identify narrowing or blockages.
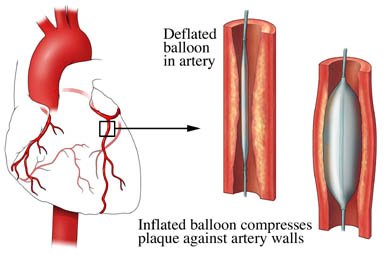
Coronary Angioplasty
Coronary angioplasty is a minimally invasive technique of abdominal artery angioplasty, which is used to treat coronary arteries that are obstructed or constricted and it is the most appropriate technique used by doctors for the treatment.
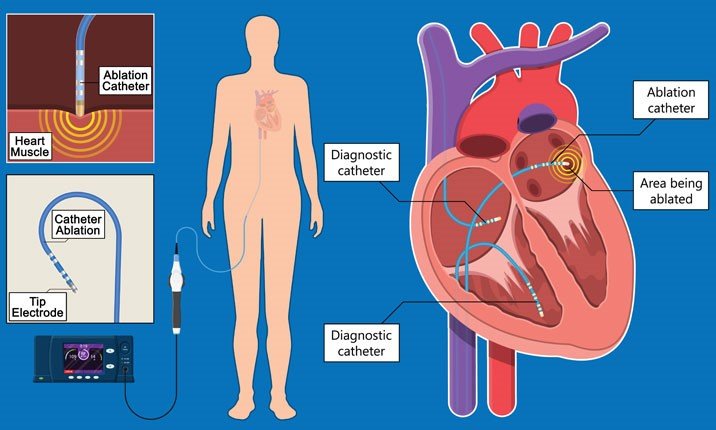
Electrophysiology Study
An Electrophysiology Study (EP study) is a test utilized to assess the heart’s electrical framework and check for abnormal heart rhythms. The natural electrical impulses coordinate the contractions of different parts of the heart.
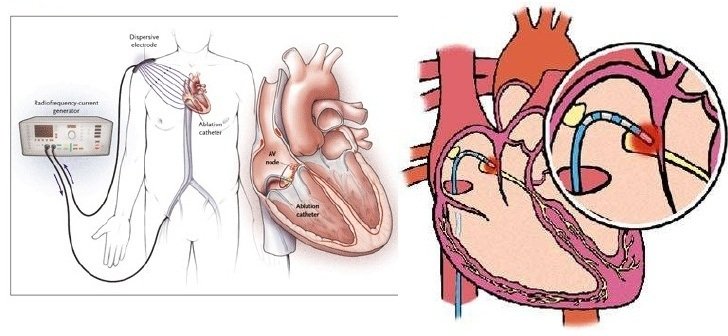
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) is a minimally invasive medical procedure that uses high-frequency electrical currents to generate heat, effectively destroying abnormal tissue or cells.
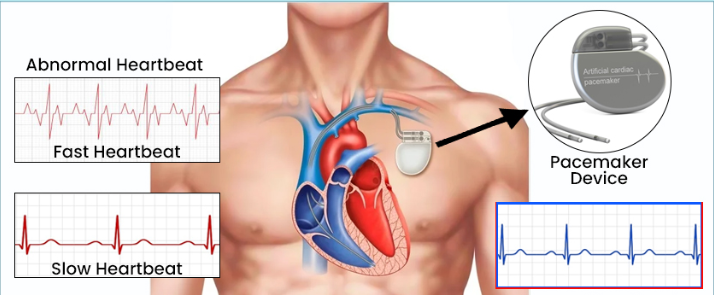
Pacemaker Implantation
Pacemakers are medical devices designed to support and regulate the electrical system of the heart, ensuring it functions properly. This medical procedure entails the insertion of a small device into the chest region.

Best Cardiologist in Nagpur
Introducing Dr. Chetan Rathi, a distinguished Cardiologist in Nagpur, whose eminence transcends the realm of medical proficiency.

CRT_P & CRT-D Implantation
CRT implantation is a process in which technological instruments known as CRT-P and CRT-D where p stands for pacemaker and d stands for defibrillator.

Valvuloplasty
A balloon mitral valvuloplasty is a process to extend a restricted heart valve and improve blood flow. The heart valves handle how blood drives through the heart.
Our Achievements in Numbers
Happy Patients
Years of experience
Specialisations
Hospital Associations
Awards & Recognition
Patient Testimonials
Dr Chetan Rathi sir is good cardiologist. I visited him many times with my family and friends for consult about issues related with cardiology.
Our Videos




Our Blog
 How Does Vitamin D Affect Your Heart?
How Does Vitamin D Affect Your Heart?
Vitamin D is much more than the “sunshine vitamin”; it is very important in the whole body of heart health. It works from bone health to an enhanced immunity function. Scientific studies show that this regulates cardiovascular health; therefore, it is a very great factor in preventing heart diseases and maintaining optimal heart function. This… Continue reading How Does Vitamin D Affect Your Heart?
Read More Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic condition that affects the way your body processes glucose, or sugar. Unchecked, diabetes mellitus can lead to serious complications, such as heart disease and kidney damage, as well as nerve problems. Understanding the types of diabetes, the symptoms of diabetes, the causes of diabetes, and how to take care of… Continue reading Understanding Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Read More What Is Syncope and How Can It Be Prevented and Treated?
What Is Syncope and How Can It Be Prevented and Treated?
Syncope, also known as fainting, is a short-lived loss of consciousness which primarily results from a sudden decrease in blood flow to the brain. Although fainting can be alarming, syncope is generally not a serious condition and can be caused by a variety of reasons; however, it may indicate an underlying serious medical condition in… Continue reading What Is Syncope and How Can It Be Prevented and Treated?
Read More



